Financial organisations that deal with deposits and borrowing services include banks. There are several different types of banks in India, each responsible for performing different functions. The deposit rate, the rate at which the general people can deposit money into the bank, is significantly lower than the lending rate, which is the rate at which the bank can lend money. You can learn more about the many types of banks in India.
What do various types of Banks do?
Although the primary tasks carried out by banks are fundamentally the same, every sector deals with a distinct population. Indian banks are responsible for the following tasks:
Accepting Public Deposits, Establishing a system for demand withdrawal, Lending Service, Transfer of funds Issuance of draughts, Facility of client lockers, and maintaining foreign exchange.
In addition to the duties listed above, the banks must also perform a variety of utility tasks.
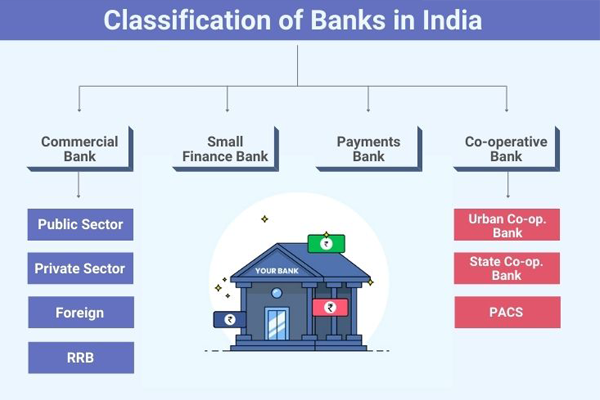
There are various different types of banks. The following describes the bank types in India:
A Payments Bank functions similarly to other banks but on a smaller scale and without putting on any credit risk. can perform the majority of banking tasks but not issue credit cards or advance loans. Demand deposits up to Rs 1 lakh can be accepted, along with mobile payments/transfers/purchases, remittance services, and other banking options like ATM/debit cards, net banking, and third-party cash transfers.
In India, small finance banks are a subset of speciality banks. Small Finance Bank (SFB) licence can offer the fundamental banking services of accepting deposits and lending. These are intended to help the unorganised sector, small businesses, marginal farmers, and other economic sectors not currently served by other banks, gain access to financial services.
A Cooperative Bank is a diminutive financial institution whose owners and clients are its members. They are registered under the States Cooperative Societies Act and are governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
The Co-operative Banks have lately made headlines due to restrictions placed by the RBI on one of the top banks, which prevented them from making any sort of cash withdrawals. The Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative Bank event (PMC) has raised questions about these financial institutions' reliability.
Commercial banks in India are known as Regional Rural Banks or RRBs. The central bank is funding RRBs' recapitalization. These banks have the authority to carry out financial transactions to encourage development and growth in rural areas.
RRB combines cooperative and commercial banks and has the following attributes: Make banking accessible and simple, support and promote regional farmers, MSMEs (medium-sized businesses), and artisans, enlist the assistance of local financial resources, operate on both a district and a state level, and among its duties are:
Give loans to MSMEs, farmers, workers, and craftspeople. accepting deposits made in savings and other types of Pension and income distribution, as well as payment offering online banking UPI offerings, Creating credit opportunities for cultural, renewable energy, and agricultural projects.
Every country has a central bank that regulates all other banks operating therein.The basic duty of the central bank includes working as the government's bank and administering and regulating all other financial institutions. Given below are the functions of a country's central bank:
Assisting other banks, stimulating the economy, implementing monetary policies and In-charge of the financial system.
To put it another way, the central bank of the country may also be described as the banker's bank because it supports the other banks in the country and regulates the financial system under the control of the government.
Commercial Banks are a type of financial organisation that provides its customers with services such as CDs, loans, overdraft protection, savings accounts, etc. Commercial Banks generate income by lending money to individuals and accumulating interest on those loans. Business loans, mortgage loans, auto loans, student loans, and personal loans, are some of the various types of loans offered by commercial banks.
Local area banks are described as little private institutions with affordable organisational models that offer financial services with geographic restrictions. These banks typically operate in three major contiguous regions, as well as rural and semi-urban areas.
The local area banks' primary goal is to mobilise rural savings through neighbourhood institutions. Additionally, they are designed to create new investment opportunities in the same local communities. Local area banks were first introduced in the Union Budget in 1996 to offer financial services locally in their neighbouring districts. These banks function as non-scheduled banks, and the Reserve Bank of India oversees and controls their operations.
These are the banks that typically work with or finance niche economic and social endeavours. These banks deal with a small group of people rather than the wider public's financing. They focus on industry-specific growth and serve a particular clientele.
Specialized banks in India typically operate with a population that is landless, agrarian, or has little rural assets. These banks offer thorough assistance for starting businesses. For instance, if a farmer visits NABARD, the bank will provide him money to purchase seeds, fertiliser, and other upkeep materials for his regular operation.